EarExternal ear : Consist of pinna, external auditory canal and tympynic membrane (TM) outer surface.
Function : It collect the sound waves n guide them to TM Pathology absence of pinna , shape deformitry, wax stone, canal stenosis, infection of hair in canal, fungal infection
Middle ear : Consist of inner surface of tympanic membrane, middle ear ossicles three in no 1. Malleus 2. Incus 3. Stapes
Function : Sound amplification, size of TM is 8 times bigger than footplate, ossicular chain hanging in middle ear.
Pthology : Middle ear fluid, perforation in ear drum with chronic infection, unsafe ear cholesteatoma, ossicular chain fixation or damage all leading to conductive deafness
Inner ear : Consists organ for heareing called cochlea and balance organ called vestibule Function : Sound processing by millions of auditory fibers for wide frequency range. Balance by utricle n sacule for lenear Accelaration. Semicircular canals for angular rotational sensation
Pathology : Permanent damage to cochlea due to high sound, infection, aging, by birth lead To sn loss. Dam,age to vestibule lead to imbalance, vertigo
AUDITORY NERVE : Exsits from cochlea joins with balance nerve(vestibular nerve) . travels through internal auditory canal along with facial nerve to enter brain stem.
FACIAL NERVE : It passes from brain – inner ear –middle ear and exit below mastoid bone to give motar supply to face muscle, eyelid muscle, muscle in lips n cheek
Function : Contraction of face muscle, taste sensation to tounge .
Pathology : facial palsy, nerve tumour, damage during surgery. Hearing Mechanism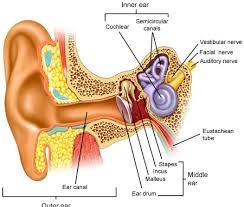 HERAING MECHANISM: Hearing is wonderful experience is’nt it . we are hearing various frequency of sounds .the sound travels in air and collected by our pinna to guide it to ear drum . the eardrum sets into vibration which are transmitted to innerear by chains of small bones namely malleus , incus and stapes. This chain is an amplifier of our hearing system as now the sound enters in inner ear fluid which is dense as compare to air. Our inner ear Is filled with fluid called endolymph which is stimulated by stapes movement and thus the wave passed in the inner ear and the point at which the wave fades stimulate the nerve ending at that point and we hear that specific frequency. Our inner ear is called chochlea . It’s a super computer which process the frequency specifically and the arrangement is such that the various frequencies are transmitted to brain, where the information is processed and various system in brain are connected to find the relevance of the information . Let’s see some examples . when we hear sound of horn we sense danger. So our system recognizes it as danger and act accordingly in fraction of seconds we adopt the position which will protect us. So in our brain that sound has to registered previously as danger sound and its stored in memory ,the action to performed in this scenario is learnt by us in past and so we act and protects our self. In above example so many systems were involved involuntarily in fraction of seconds . HERAING MECHANISM: Hearing is wonderful experience is’nt it . we are hearing various frequency of sounds .the sound travels in air and collected by our pinna to guide it to ear drum . the eardrum sets into vibration which are transmitted to innerear by chains of small bones namely malleus , incus and stapes. This chain is an amplifier of our hearing system as now the sound enters in inner ear fluid which is dense as compare to air. Our inner ear Is filled with fluid called endolymph which is stimulated by stapes movement and thus the wave passed in the inner ear and the point at which the wave fades stimulate the nerve ending at that point and we hear that specific frequency. Our inner ear is called chochlea . It’s a super computer which process the frequency specifically and the arrangement is such that the various frequencies are transmitted to brain, where the information is processed and various system in brain are connected to find the relevance of the information . Let’s see some examples . when we hear sound of horn we sense danger. So our system recognizes it as danger and act accordingly in fraction of seconds we adopt the position which will protect us. So in our brain that sound has to registered previously as danger sound and its stored in memory ,the action to performed in this scenario is learnt by us in past and so we act and protects our self. In above example so many systems were involved involuntarily in fraction of seconds .
- Hearing center : to identify that particular frequency.
- Memory center: to recollect importance of that sound.
- Motar system : muscle stimulation system to perform the action of body parts.
- Sympathetic system : because of which our heart rate increases we sweat. BUT IMMAGINE IF YOU CAN’T HEAR THE HORN No system is stimulated and you may face danger. So we should know why hearing is affected.
- Cerebellum (small brain): for smooth action in complex movement from legs to complete body
|

 HERAING MECHANISM: Hearing is wonderful experience is’nt it . we are hearing various frequency of sounds .the sound travels in air and collected by our pinna to guide it to ear drum . the eardrum sets into vibration which are transmitted to innerear by chains of small bones namely malleus , incus and stapes. This chain is an amplifier of our hearing system as now the sound enters in inner ear fluid which is dense as compare to air. Our inner ear Is filled with fluid called endolymph which is stimulated by stapes movement and thus the wave passed in the inner ear and the point at which the wave fades stimulate the nerve ending at that point and we hear that specific frequency. Our inner ear is called chochlea . It’s a super computer which process the frequency specifically and the arrangement is such that the various frequencies are transmitted to brain, where the information is processed and various system in brain are connected to find the relevance of the information . Let’s see some examples . when we hear sound of horn we sense danger. So our system recognizes it as danger and act accordingly in fraction of seconds we adopt the position which will protect us. So in our brain that sound has to registered previously as danger sound and its stored in memory ,the action to performed in this scenario is learnt by us in past and so we act and protects our self. In above example so many systems were involved involuntarily in fraction of seconds .
HERAING MECHANISM: Hearing is wonderful experience is’nt it . we are hearing various frequency of sounds .the sound travels in air and collected by our pinna to guide it to ear drum . the eardrum sets into vibration which are transmitted to innerear by chains of small bones namely malleus , incus and stapes. This chain is an amplifier of our hearing system as now the sound enters in inner ear fluid which is dense as compare to air. Our inner ear Is filled with fluid called endolymph which is stimulated by stapes movement and thus the wave passed in the inner ear and the point at which the wave fades stimulate the nerve ending at that point and we hear that specific frequency. Our inner ear is called chochlea . It’s a super computer which process the frequency specifically and the arrangement is such that the various frequencies are transmitted to brain, where the information is processed and various system in brain are connected to find the relevance of the information . Let’s see some examples . when we hear sound of horn we sense danger. So our system recognizes it as danger and act accordingly in fraction of seconds we adopt the position which will protect us. So in our brain that sound has to registered previously as danger sound and its stored in memory ,the action to performed in this scenario is learnt by us in past and so we act and protects our self. In above example so many systems were involved involuntarily in fraction of seconds .